Each tumor has its own microbiota
Not all tumor microbiomes are the same, with bacteria varying in frequency and diversity depending on tumor type. This is particularly so since each type of cancer (breast, lung, brain, bone, etc.) has its own specific signature.
Lay public section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
About this article
The presence of bacteria in human tumors is no new discovery: we have known about it for over a century. Despite this, due to its low biomass, little is really known about the tumor microbiota. Using a combination of multiple technologies, a team of researchers has studied 1,010 tumor samples and 516 samples of healthy adjacent tissue, with a total of seven tumor types screened: breast, lung, ovarian, pancreatic, melanoma, bone, and brain.
Bacteria in tumors and macrophages
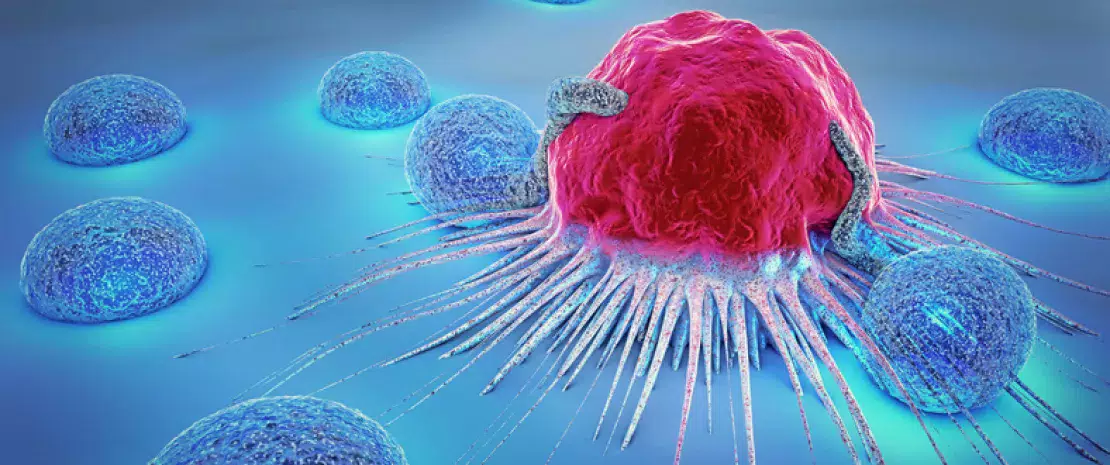
First finding: the frequency of bacterial DNA detection depends on the type of tumor, from 14.3% for melanoma to over 60% for breast, pancreatic and bone cancers. A study of more than 400 additional tumors has confirmed bacterial components (16S rRNA and (sidenote: Lipopolysaccharides Molecules found in the outer membrane of bacteria ) ) to be frequently present in both cancer cells and adjacent immune cells. On the other hand, the detection of spherical or rod-like bacteria was rare, suggesting a possible alteration of the envelope of intra-tumoral bacteria.
A specific microbiota for each cancer
Second finding: breast cancer has a particularly rich and diverse microbiota, with an average of 16.4 bacterial species detected per tumor, compared to less than 9 for other types of cancer. The culture of fresh tumor samples appears to confirm that these bacteria thrive. More importantly, each type of tumor has a distinct bacterial composition. For example, species belonging to the Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes phyla are the most frequent in colorectal tumors, whereas Proteobacteria predominate in pancreatic cancer.
A niche effect
Lastly, metabolic activities of intra-tumoral microbiota are highly dependent on the type of tumor. For example, in lung cancer, there is an increase in the number of bacteria capable of breaking down the chemicals present in cigarette smoke (toluene, acrylonitrile, etc.). According to the researchers, high concentrations of these metabolites may create a niche favorable to bacteria capable of metabolizing them.
Manipulating the tumoral microbiota?
At this stage, the study does not tell us whether bacteria play a causal role in the development of a tumor, or whether the tumor itself is responsible for their presence (the tumor may disorganize the vascular system, allowing bacteria to penetrate its cells). However, just as other studies have shown the gut microbiota to influence response to (sidenote: Immune checkpoints are used by tumors to protect themselves from immune system attacks and may be blocked by ICI therapy in order to restore the immune system function. ) , the researchers hope that by manipulating the tumoral microbiota it may be possible to alter the tumor’s defenses and, therefore, its response to immunotherapy. Indeed, the microbiota of melanoma varies between patients who respond well or poorly to immunotherapy. This creates hope for new diagnostic tools or even treatment methods.