Do antibiotics make gut microbiota less resilient?
Even in healthy volunteers, short courses of antibiotics would be sufficient to disrupt their gut microbiota. As a result, these treatments can leave short- and long-term "scars” with long-lasting antibiotic resistance.
Lay public section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
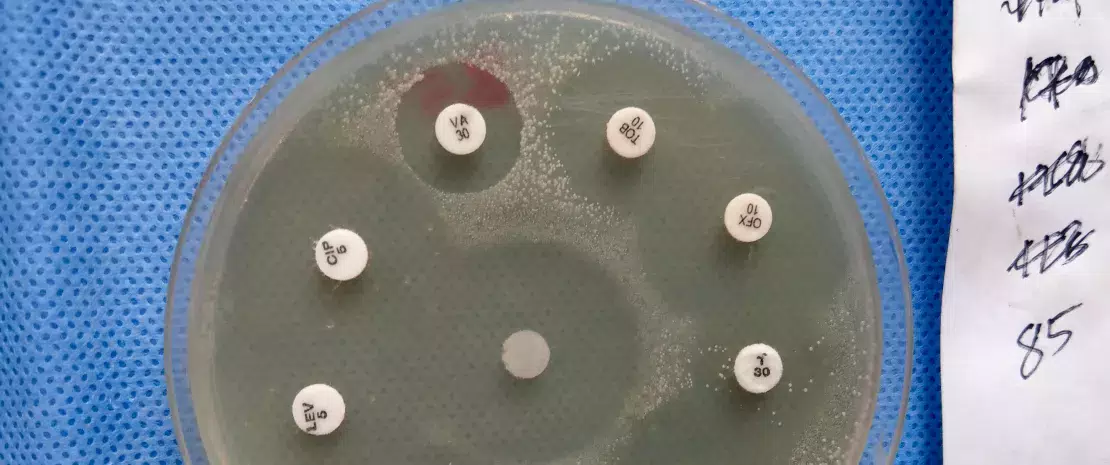

About this article
Medical research on the impact of antibiotics is hindered by the fact that the studies are generally carried out on polymedicated sick and hospitalized patients. As such, various confounding factors (infection, medications, hospital environment, potential immunosuppression) skew the observations.
The only solution is to conduct prospective studies on healthy outpatient adults, such as this one. American researchers measured the impact of four antibiotic treatments, namely azithromycin (AZM), levofloxacin (LVX), cefpodoxime (CPD) or a combination of CPD and AZM), on the gut microbiota of 20 healthy volunteers randomized into four groups by collecting their stools before, during and two months after the end of treatment (15 collection points in all).
Antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis
First finding: antibiotics reduce bacterial abundance and diversity. Depending on the treatment received, changes in abundance differed :
- higher levels of both Bacteroidetes and Clostridium for patients receiving CPD or CPD + AZM at Day 6,
- higher levels of Firmicutes, such as Eubacterium, Ruminococcus and Anaerostipes, for those receiving LVX or AZM.
In addition, AZM (alone or in combination), which has a long half-life, delays the recovery of bacterial abundance, eight bacterial species and some associated metabolic pathways compared to other antibiotics.
What is the World Antimicrobial Awareness Week?
Each year, since 2015, the WHO organizes the World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW), which aims to increase awareness of global antimicrobial resistance. Held on 18-24 November, this campaign encourages the general public, healthcare professionals and decision-makers to use antimicrobials carefully, to prevent the further emergence of antimicrobial resistance.
A reservoir of resistance genes
Another effect of the antibiotics was the emergence of a long-lasting reservoir of resistance genes in volunteers receiving CPD, AZM and CPD+ AZM treatments, in contrast to those receiving LVX. However, more importantly, the altered composition of their resistome would lead to an increase in three genes (tetO, cfxA, and tet40), two of which do not confer resistance to the antibiotics administered.
Resilience varies from person to person
Lastly, for 17 of the volunteers, dysbiosis induced by antibiotics was only moderate and transitory, with the microbiota returning to their pre-treatment balance within a few weeks. In contrast, in three volunteers with an initially low diversity of gut microbiota, antibiotic treatment induced a more pronounced dysbiosis (to the point of presenting similarities with patients in intensive care) and some of the imbalances were still present at the end of the follow-up period, i.e. 2 months post-treatment. Hence the need for the judicious use of antibiotics.
Consequently, antibiotic disruption appears to create opportunities for bacteria with broad resistance. For example, Bacteroides that survive CPD treatment, probably via ß-lactam resistance gene cfxA, would create a low-diversity, high-Bacteroides environment, favourable to pathogens such as Enterobacter. Short courses of antibiotics could trigger the acquisition or entrenchment of diverse resistance genes.
Meet Professor Sørensen, 2022 Biocodex Microbiota Foundation International Grant Winner.
His team pioneered an ambitious study on the resistome of 700 children that will facilitate a breakthrough in the understanding of the evolution and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in the early life human gut.