The Janus face of Antibiotics: Life Savers and Microbiota Disruptors
A page turns: with the advent of antibiotics in the 20th century, this type of therapy, despite its undoubted usefulness in fighting infections, now raises serious concerns for health, notably with microbiota dysbiosis and antibiotic resistance.
Lay public section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
Sections
About this article
Introduction
Though a more rational use of antibiotics has long been overdue, we must not lose sight of the fact that over the course of the last 80 years their widespread use has saved many millions of lives. They have served as our principal weapon in the fight against bacterial infections. Alongside vaccinations, they have added around 20 years to the average life.1
18 out of 1,000
"18 out of 1,000 people take antibiotics every day.”5
FROM THE ANTIBIOTIC ERA TO THE MICROBIOTA ERA
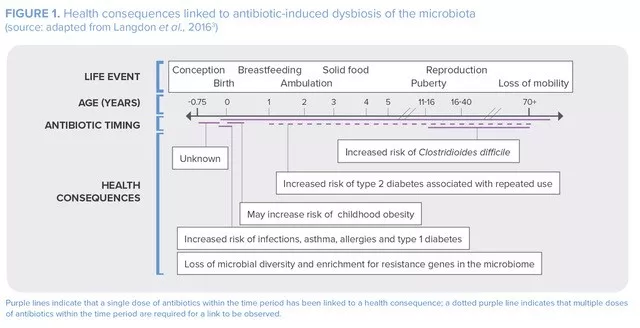
Unfortunately, antibiotics eliminate not only pathogenic bacteria, but commensal ones too.2 The intestinal microbiota is affected, and likewise all the other human microbiota (cutaneous, lung, urogenital...) that protect against pathogen overgrowth. While it remains difficult to define a healthy microbiota with any precision or to provide an adequate description of dysbiosis, science is beginning to understand the ways in which antibiotics affect the functioning of these ecosystems and likewise the consequences of such changes for health over the short and long term3 (See Figure 1).
Dysbiosis
"Dysbiosis" is not a homogenous phenomenon: it varies according to the state of health of each individual. It is commonly defined as a compositional and functional alteration in the microbiota, driven by a set of environmental and host-related factors that perturb the microbial ecosystem.4
ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE, A GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH PROBLEM
Because of the widespread overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals, bacteria causing both benign and life-threatening infections are becoming increasingly resistant to them. In 2015, antibiotic-resistant pathogens were estimated to be causing over 50,000 deaths each year in Europe and the United States.3 “Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health, food security and development today” states the WHO.
5 World Health Organization. WHO report on surveillance of antibiotic consumption: 2016-2018 early implementation. Geneva; 2018.