The ENT microbiota
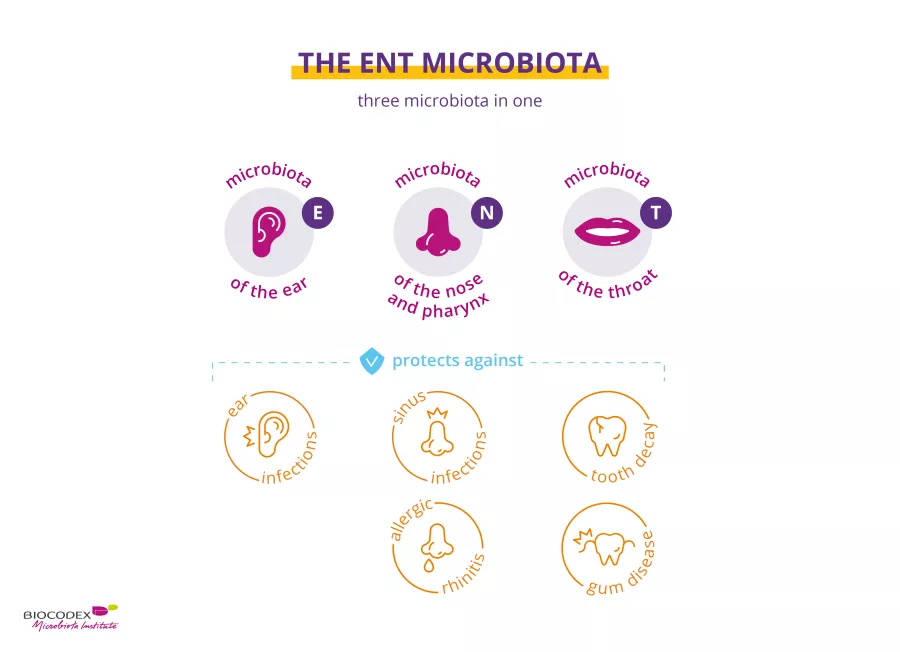
The ENT (ear, nose, throat) microbiota is made up of three distinct bacterial floras: the oral microbiota, the auricular microbiota, and the nasopharyngeal microbiota.
Various diseases can result from their imbalance.
- Learn all about microbiota
- Microbiota and related conditions
- Act on your microbiota
- Publications
- About the Institute
Healthcare professionals section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
Sections

About this article
The term ENT includes three parts of the body: Ears, Nose, and Throat (which also includes the mouth).
- The oral microbiota brings together more than 700 bacterial species, which contribute to oral health (teeth, gums, tongue, etc.) and, more generally, to overall health. A disruption in this equilibrium (dysbiosis), resulting from poor oral hygiene, a drop in immunity, or a genetic origin may lead to local infections (cavities, periodontitis, etc.) that are likely to migrate or cause more serious diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases. Hygiene and dental care remain the most effective method of prevention.
- In the ear canal, the composition of the auricular microbiota is closely related to that of the skin. Recent work has shown the harmless presence of Alloiococcus otitis and Corynebacterium otitidis, two bacterial species that until now have only been associated with middle ear infections. This discovery suggests that the ear canal serves as an infectious reservoir for the middle ear.
- Although close to the oral microbiota, the nasopharyngeal microbiota, which covers the nasal airways and the pharynx, is composed of very different germs.
Analyzing the realm of ENT and its microbiota may enable early diagnosis for various diseases that appear because of (sidenote: Dysbiosis Generally defined as an alteration in the composition and function of the microbiota caused by a combination of environmental and individual-specific factors. Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, et al. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(4):219-232. ) and may also contribute to the development of personalized medicine based on probiotics.
International Microbiota Observatory
The Biocodex Microbiota Institute is dedicated to education about human Microbiota for General Public and Healthcare Professionals, it doesn't give any medical advice.
We recommend you to consult a healthcare professional to answer your questions and demands.
Arweiler NB, Netuschil L. The oral microbiota. A. Schwiertz (ed.), Microbiota of the Human Body, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 902.
Kloos, WE, Schleifer KH. "Staphylococcus auricularis sp. nov.: an Inhabitant of the Human External Ear". International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 1983 ; 33 (1): 9–14.