6 essential things you should know about antibiotics
On the positive side, they are the mainstay in our therapeutic arsenal, saving millions of lives every year. On the flip side, they disrupt our microbiota and can have serious consequences on our health. Review of 6 key tips to use them wisely.
- Learn all about microbiota
- Microbiota and related conditions
- Act on your microbiota
- Publications
- About the Institute
Healthcare professionals section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information

About this article
1. Antibiotics save lives
Since the discovery of penicillin in 1928, the widespread use of antibiotics has saved millions of lives. The main weapon in the fight against bacterial infections, antibiotics, alongside vaccinations, have added nearly twenty years to life expectancy.1

2. Antibiotics destroy species responsible for infections, but also eliminate good bacteria
Gut, vagina, lungs, skin... many parts of the body play host to (sidenote: Microorganisms Living organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea and protozoa, and are commonly referred to as “microbes”. What is microbiology? Microbiology Society. ) (bacteria, fungi, viruses). Such microbial communities are known as microbiota.2 Antibiotics eradicate pathogenic germs responsible for infection but can also destroy certain beneficial bacteria in our microbiota, leading to imbalances ( (sidenote: Dysbiosis Generally defined as an alteration in the composition and function of the microbiota caused by a combination of environmental and individual-specific factors. Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, et al. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(4):219-232. ) )3 of varying degrees within these ecosystems.
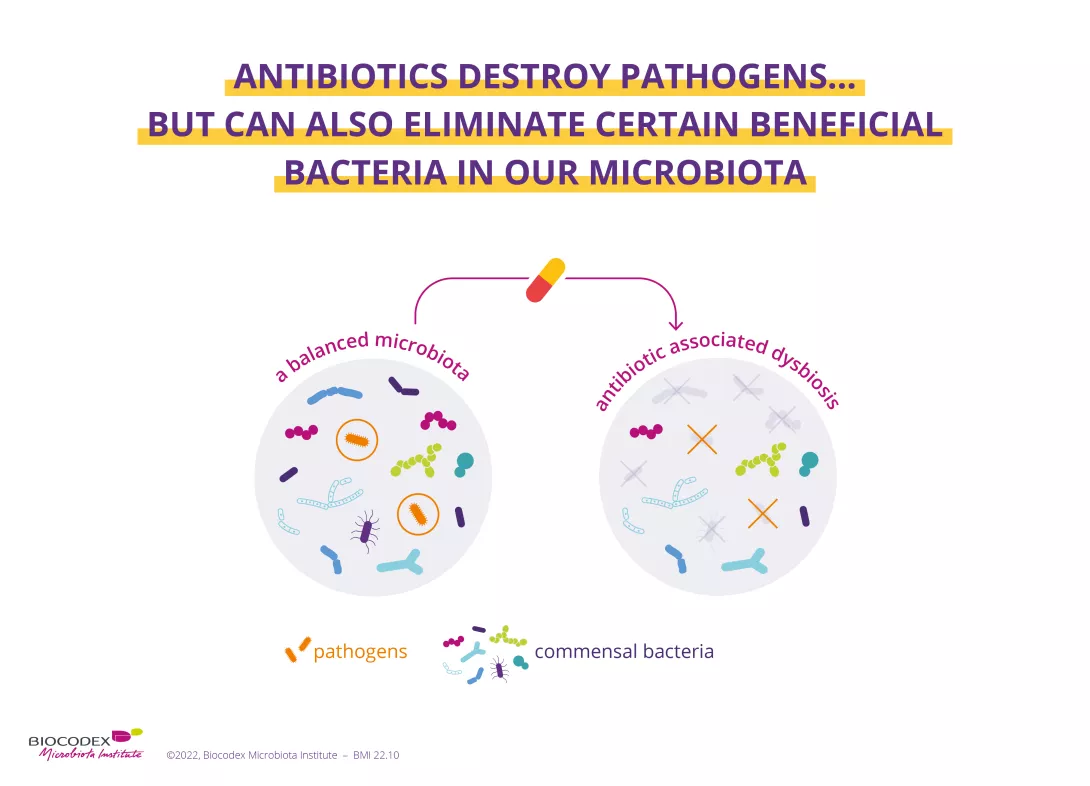
This concerns all of the body’s microbiota, including:
- the gut microbiota,
- the skin microbiota,4
- the lung microbiota,5
- the ENT microbiota,6
- the urinary microbiota,7
- and the vaginal microbiota.8
3. Antibiotics can have side effects
By inducing a dysbiosis, antibiotics can have harmful effects on health. The main short-term complication is the alteration of bowel movements experienced by some patients. This most often results in diarrhea, with the gut microbiota less able to perform its protective functions. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is usually mild to moderate9 in intensity, but its incidence varies according to age, type of antibiotic, context, etc. It may affect up to 35%9,10,11 of patients and 80% of children.9 In 10%-20% of cases, the diarrhea results from an infection by Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile),11 a bacterium that colonizes the gut microbiota and becomes pathogenic due to certain factors (e.g. antibiotic use). The clinical consequences vary, ranging from moderate diarrhea to much more serious symptoms, or even death.11
35% Antibiotic-associated diarrhea may affect up to 35% of patients
80% and up to 80% if patients are children
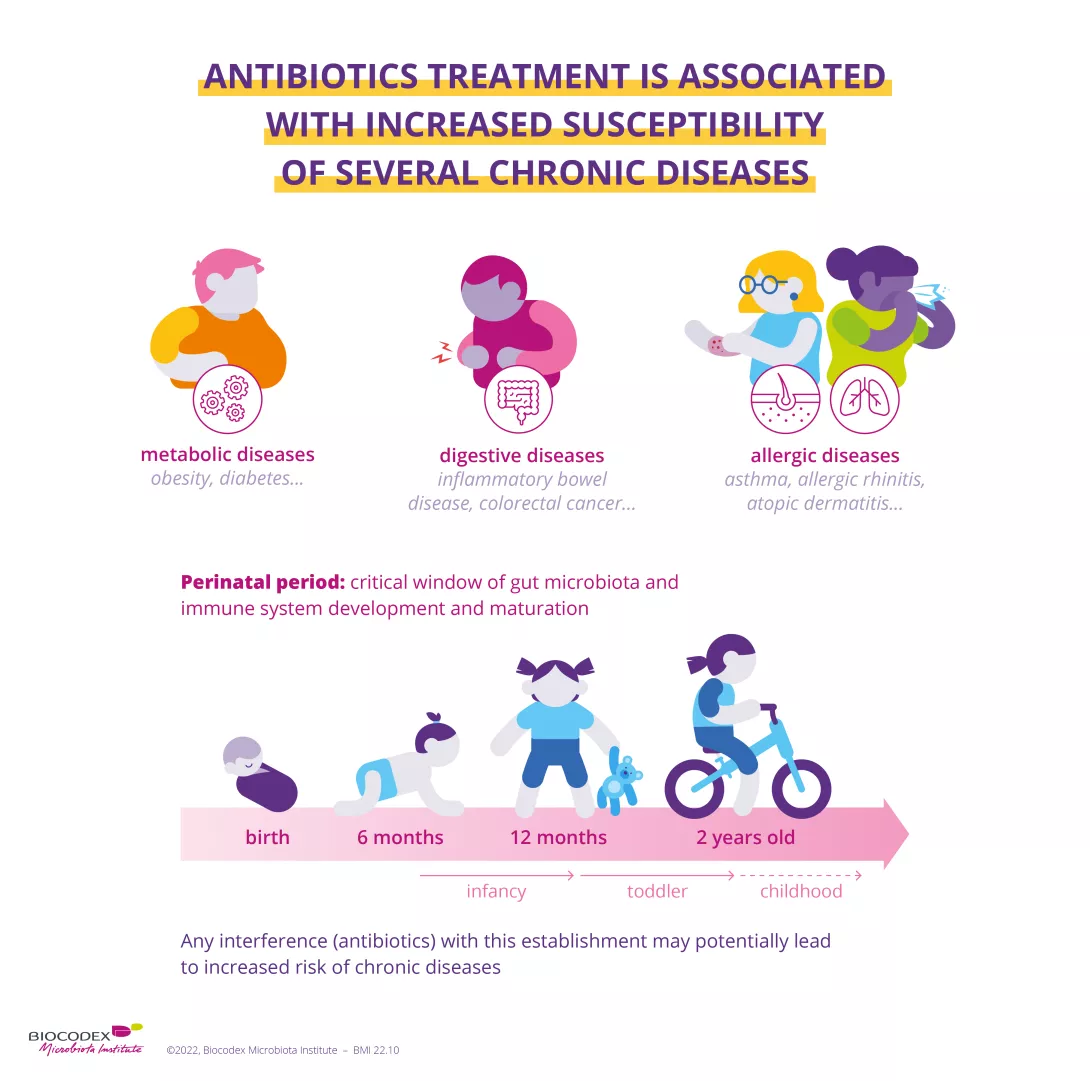
4. Antibiotics are thought to be responsible for longer-term effects
Diarrhea is not the only symptom of antibiotic-associated dysbiosis. When it occurs early in life, the condition is thought to be responsible for longer-term effects. The perinatal period, characterized by the development of the gut microbiota and the maturation of the immune system, is a particularly sensitive period.12 Antibiotic-associated dysbiosis during this phase seems to be a risk factor in the development of certain chronic diseases (obesity, diabetes mellitus, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease).13
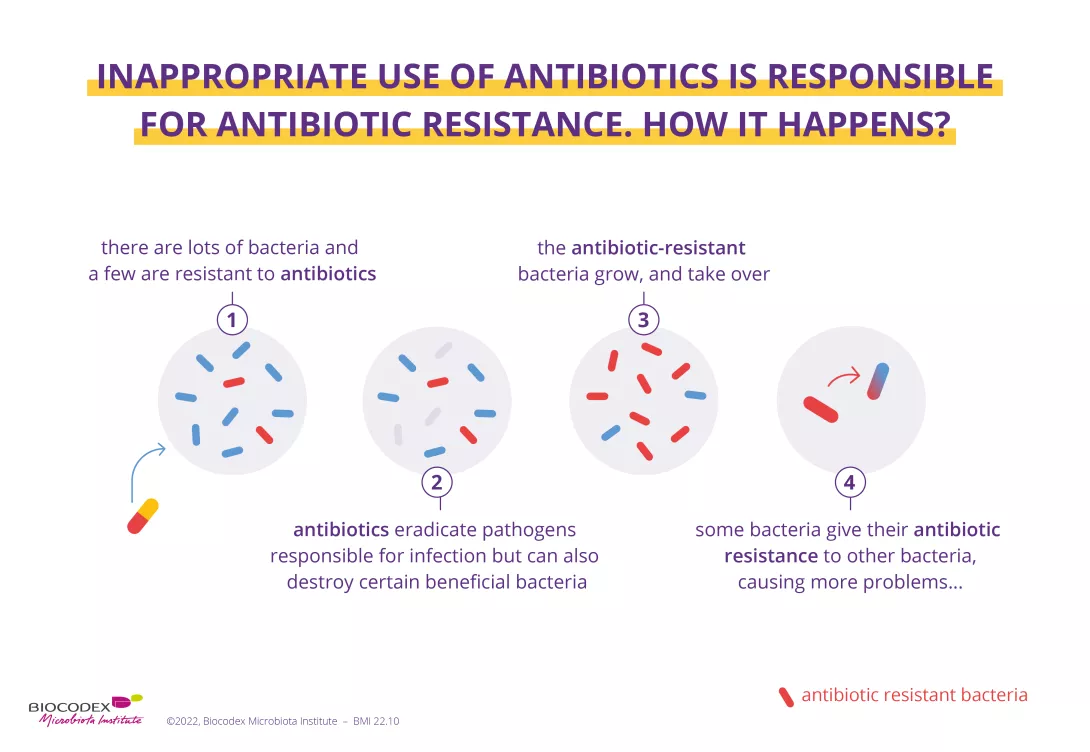
5. Inappropriate use of antibiotics is responsible for antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance happens when an antibiotic treatment is no longer effective against a bacterial infection.1 The cause? Antibiotics are only effective against bacteria and have no effect on viruses (e.g. the flu).14 The inappropriate (e.g. with viral infections) or excessive use of antibiotics – in humans or animals – accelerates antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance leads to longer hospitalizations, higher health care costs and more deaths. For this reason, the issue has become a major public health concern worldwide.1
6. World AMR Awareness Week
Each year, from November 18 to 24, the WHO organizes World AMR Awareness Week, which aims to increase awareness of global (sidenote: Antimicrobial Class of drugs that includes antibiotics (active against bacteria), antiviral agents (active against virus), antiparasitic agents (active against parasites), and antifungal agents (active against fungi). WHO Antimicrobial Resistance; Oct 2020 ) resistance and to encourage best practices among the general public, health workers and policymakers to avoid the further emergence and spread of drug-resistant infections. As an expert on microbiota, the Biocodex Microbiota Institute takes part in this initiative.
If you are interested in the effects of antibiotics on your health and your microbiota, or if you want to know more about the World AMR Awareness Week (WAAW), we recommend that you go to this other dedicated page:
Antibiotics: what impact on the microbiota and on our health?
Each year, since 2015, the WHO organizes the World AMR Awareness Week (WAAW), which aims to increase awareness of global antimicrobial resistance.
Antimicrobial resistance occurs when bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi change over time and no longer respond to medicines. As a result of drug resistance, antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines become ineffective and infections become increasingly difficult or impossible to treat, increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
Held on 18-24 November, this campaign encourages the general public, healthcare professionals and decision-makers to use antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals and antiparasitics carefully, to prevent the further emergence of antimicrobial resistance.
1. WHO Antimicrobial Resistance; Oct 2020; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance
9. McFarland LV, Ozen M, Dinleyici EC et al. Comparison of pediatric and adult antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile infections. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(11):3078-3104.
10. Bartlett JG. Clinical practice. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med 2002;346:334-9.
11. Theriot CM, Young VB. Interactions Between the Gastrointestinal Microbiome and Clostridium difficile. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015;69:445-461.
14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Patient Education and Promotional Resources https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/community/pdfs/aaw/au_improving-antibiotics-infographic_8_5x11_508.pdf