The skin microbiota
The skin microbiota: why is it so important?
- Learn all about microbiota
- Microbiota and related conditions
- Act on your microbiota
- Publications
- About the Institute
Healthcare professionals section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
Sections

About this article
Table of contents
Table of contents
35% only 1 in 3 people knew that it was better not to wash twice a day to preserve their skin’s microbiota
What exactly is the skin microbiota?
Let’s start by focusing on the skin, the largest organ in the human body and its first line of defense. The skin acts as a triple protective barrier:1,2
- a physical barrier that protects the internal organs from the external environment3
- a chemical barrier: dry and rich in salt and acidic compounds, the skin is a hostile environment for many microorganisms4
- an immune barrier, thanks to defense cells in the skin that prevent colonization and infection by pathogenic microbes2
Despite this, the skin is home to its own distinctive microbiota which includes bacteria (Cutibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus epidermidis, etc.), fungi (e.g. Malassezia), viruses (e.g. papillomavirus) and parasites (including mites such as Demodex). These microorganisms live in perfect harmony and together form the skin microbiota.1,5
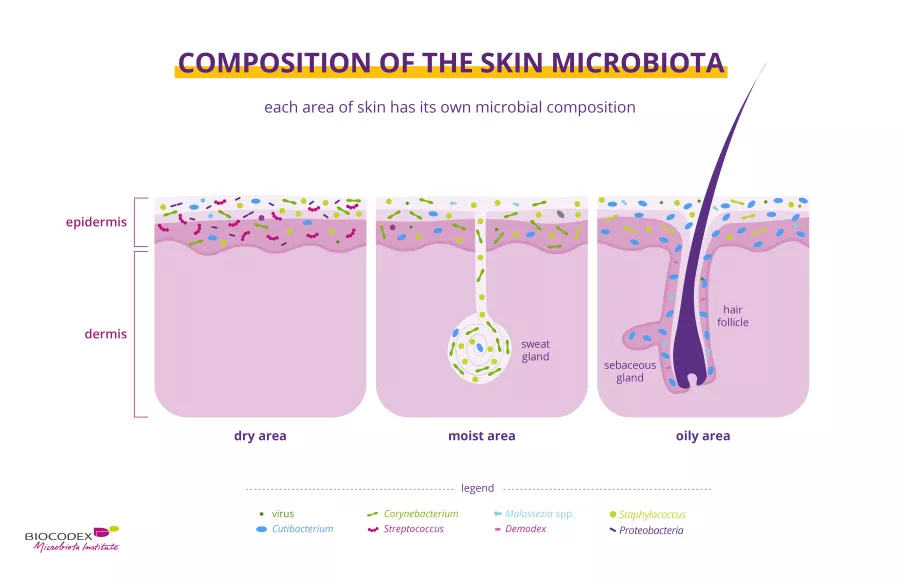
As you may have noticed, your skin changes from one part of the body to another:
- drier on the forearm and the palms of the hand.1,5
- oilier on the face, chest and back.1,5
- and more humid in the armpits, the elbow fold, the nostrils, on the back of the knee and on the groin.1,5
Each of these skin sites is home to a distinct microbiota adapted to its specific environment1. Some researchers also distinguish a fourth site in the foot (nails, heel and space between toes).1
In addition to these variations across the skin’s surface, there are also variations according to depth or skin layer: the deeper you go into the dermis, the fewer the
(sidenote:
Microorganisms
Living organisms too small to see with the naked eye. This includes bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, protozoa, etc., collectively known as ’microbes’.
Source: What is microbiology? Microbiology Society.
)
and the more similar these microorganisms are from one person to next.6
How does the skin microbiota change throughout life?
The skin microbiota is relatively stable over time1,5 and only changes at the major stages of life.
At birth, children born vaginally are passed on vaginal bacteria (Lactobacillus, C. albicans), while those born by caesarean section receive skin microbes (Staphylococcus, Streptococcus). At puberty, the rate of secretion of growth hormones explodes. The skin becomes oilier and selects more well-adapted microorganisms that live on through adulthood. The skin gradually changes as it ages, with a weakened immune system, reduced cell renewal, less sweat, and altered sebum production.7,8
These physiological changes modify the skin environment and alter the microbial balance7, which becomes more diverse and sees a change in dominance in bacterial groups.8
Why is the skin microbiota a key factor in skin health?
The skin microbiota knows how to thank its host for giving it food and shelter. It protects the host from (sidenote: Pathogens A pathogen is a microorganism that causes, or may cause, disease. Pirofski LA, Casadevall A. Q and A: What is a pathogen? A question that begs the point. BMC Biol. 2012 Jan 31;10:6. ) through its physical presence on the skin and by secreting antibacterial molecules and acids.2 But that’s not all. The skin microbiota also plays a key role in immunity: it stimulates the immune defense mechanisms of the epidermis and the body as a whole and calms inflammation where necessary.4
What diseases are associated with an unbalanced skin microbiota?
The composition of the skin microbiota is mostly influenced by host characteristics (age, sex, genes, immune status, diet, stress levels) and the environment (lifestyle, domestic and personal hygiene, living arrangements, geographical location, sun exposure, etc.).2 At times, factors such as stress, a lifestyle change or the use of medication (e.g. antibiotics) or personal hygiene products disrupt the balance of the microbiota: bacteria previously beneficial to the host take the upper hand and become pathogenic.1 Many common skin diseases are associated with changes in the microbiota. This situation is known as a (sidenote: Dysbiosis Generally defined as an alteration in the composition and function of the microbiota caused by a combination of environmental and individual-specific factors. Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, et al. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(4):219-232. ) .1
Dysbiosis is often associated with pathological skin conditions such as acne,9 atopic dermatitis,10 psoriasis,11 seborrheic dermatitis,12 rosacea13 or skin cancer.14 Changes in the skin microbiota can also be observed in non-pathological skin conditions such as sensitive skin, sensations of discomfort or irritation, or diaper rash. The skin is constantly exposed to various external factors linked to lifestyle (cold, heat, sun, UV, hygiene products, etc.) or the individual (genes, sensitivity, allergies, etc.) that can affect the physical, mechanical or microbial properties of the skin barrier.15 The microbiota is also involved in wound healing16 and body odor.17
The gut-skin axis
The gut and the skin are intimately linked. The communication channel between them is known as gut-skin axis. Several common skin diseases, such as acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and rosacea have been associated with gut dysbiosis.18
How can you take care of your skin microbiota?
You now know the importance of the skin microbiota for the health of your skin, and that the gut microbiota also plays a role in skin health. So how can you take care of the various microbiota so that your skin stays healthy? Many researchers have looked into this question. Unfortunately, the answer isn’t as straightforward as using beneficial bacteria or yeast to replenish or enrich the existing microbiota or replace a microbiota that’s not up to the job. Instead, the idea is to modify the microbiota so that it functions correctly, thus improving host health. How? There are several ways to improve the balance and diversity of the gut microbiota, each with its own characteristics:
Oral preparation:
The existence of a gut-skin axis raises hope that we may be able improve the health of the skin by modulating the gut microbiota by taking probiotic, prebiotic and symbiotic supplement or through a better diet:
- Probiotics are living microorganisms that confer a health benefit on the host when applied in appropriate quantities19,20. For certain inflammatory skin diseases, the use of specific probiotics appears to be effective.14
- Prebiotics are specific non-digestible dietary fibers that confer a health benefit. They are selectively used by beneficial microorganisms in the host microbiota.21,22 Symbiotics23 mixture containing both prebiotic and probiotic have shown promising results in atopic dermatitis.24
- Diet, the diversity and quality of what we eat contributes to the balance of our gut microbiota.25,26 A poorly balanced diet can affect the composition of the gut and give rise to certain conditions.27 To keep our gut in shape we should know what foods have a beneficial or adverse effect on it.28
Topical preparations
While few studies existed, products applied to the skin that contain certain probiotics, prebiotics or both, have shown positive resulted in improving the skin's health of patient with skin condition.14,24
However, clinical trials are still required to optimize their formulation. Hence the importance of following our latest news on the skin microbiota.
All the information in this article comes from scientific approved sources. Keep in mind this is not exhaustive. Here are all the studies from which we took all of that information.