Mood disorders
Depression and bipolar disorder indicate a mood disorder. Beyond classic psychiatric treatments, research is in progress to evaluate the impact of intestinal microbiota on these disorders.
The gut microbiota
Depression and bipolar disorder indicate a mood disorder. Beyond classic psychiatric treatments, research is in progress to evaluate the impact of intestinal microbiota on these disorders.
The gut microbiota
Certain anxiety disorders, which a great number of people suffer from, may be linked to activity in the gastrointestinal microbiota through the regulation of stress hormones. The discovery of the role of the microbiota in anxiety disorders allows us a glimpse of new potential avenues for treatment.

Autism-spectrum disorders (ASDs) refer to the collection of neurobiological diseases that affect social interactions. They may have a gastrointestinal origin.

Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease in France. It progressively destroys the dopamine neurons in the brain. A link to a disruption in intestinal microbiota has been shown.
The gut microbiota
Alzheimer's disease, whose factors are still poorly understood, still has no effective treatment. However, a hypothesis around the role of the intestinal microbiota is emerging, sparking hope for new therapeutic avenues.

Prostatitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the prostate. It can be caused by infection, in the case of acute inflammation. The responsible bacteria is most often Escherichia coli. Chronic pain, however, more likely implies an imbalance in the urinary microbiota.
The urinary microbiota
Cystic fibrosis is a rare genetic disease that manifests through serious respiratory and digestive problems. There appears to be a connection between these symptoms and the gastrointestinal microbiota.
The ENT microbiota
Cold, bronchitis, strep throat... It’s hard to get through the winter without being affected by at least one of these respiratory infections. In terms of prevention, probiotic therapy may stimulate immune defenses.
The pulmonary microbiota
The presence of a certain family of bacteria in the gut microbiota may be involved in the recurrence of Crohn’s disease following bowel resection. Can the presence of these bacteria predict recurrence?
The gut microbiota Dysbiosis confirmed in paediatric crohn's disease Crohn’s disease: gut dysbiosis seems to precede flares Crohn’s disease: is the ileal microbiota a predictive factor of recurrence?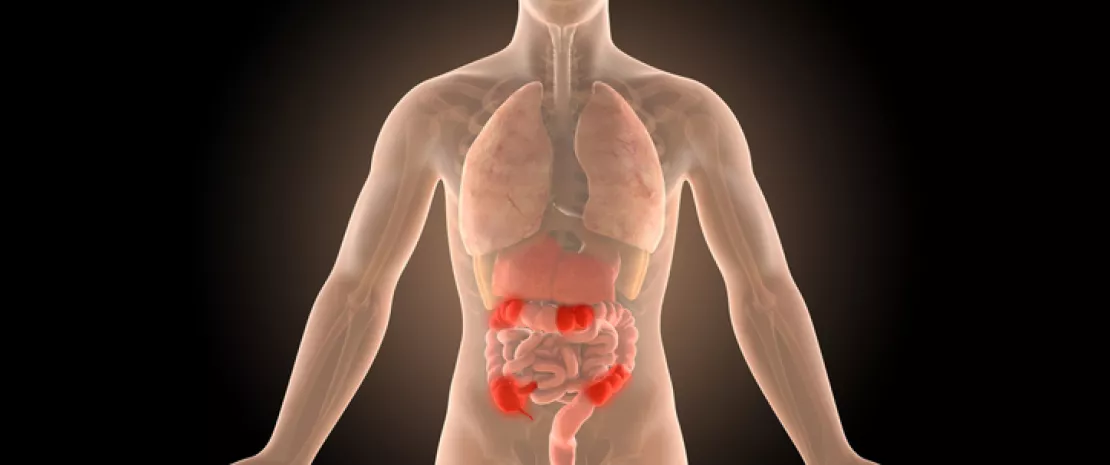
One of the main target organs for SARS-CoV-2 other than the lungs is the intestines, which also act as a potential dissemination route. Hence this review focusing on gastrointestinal disorders and the role of the gut microbiota in Covid-19 symptoms and mortality.
The gut microbiota Covid-19: gut microbiota involved? How does Covid-19 affect the gut microbiota? Gut dysbiosis in SARS-CoV-2 infected monkeys